Minimum Set Primers and Unique Probes Design Algorithms for
Differential Detection of Symptom-Related Pathogens
| HOME | |
| Introduction | |
| Methodology | |
| Tetra-Nucleotide Nucleation (TNN) | |
| Unique & Common Sections | |
| Nearest-Neighbor Model | |
| MCGA | |
| Linker Design | |
| Computational Results | |
| Bio-Experiment | |
| Conclusion | |
| Reference | |
The designs of primers and probes share many common techniques. Among them, identifying common and unique regions on the target sequences is one of the major tasks. Several criteria are applied for the selection of unique and common sequences on the target sequences. We have noticed from our observations that unique sequences are likely near common sections. That is, on DNA sequences, tetra-nucleotides with high and low occurrences in target dataset will reside to each other. A unique region in a sequence is lead and followed by regions common to many sequences. Therefore the candidates for primers and probes are located on nearby regions on target sequences. Based on this assumption, we designed our algorithm to select unique and common sections on any given sequence. We have used two values to indicate the density of unique TNN in a region ( U d ) and aggressions of these unique TNN ( U a ) (Chang and Peck, 2003) :
Where N uniq is the number of unique tetra-nucleotide in the sequence, and L is the length of the region. The position of the initial base of the i th unique TNN is given by x i . Also, x 0 = 0, x n+1 = L , and n = N uniq . The high density of unique TNN ( U d ) and low aggression of unique TNN ( U a ) have been shown to be good indications for high specificity probes (Chang and Peck, 2003) . Regions with large U d values are selected; these regions are much more specific to the given sequence. If the distribution of unique TNN were uniform in the sequence, the value of U a will approach 0. A lower U a value indicates that the unique TNNs overlap less with each other. Here we proposed a modified score for selection of unique and common regions on the target sequences:
The two weights a and b can be arbitrarily selected for selection of unique and common regions, respectively. In this work, we chose equal weights for the two values. The selected region is more unique if the score is higher. Likewise, if the common regions are selected, the score ( S ) should be minimized. |
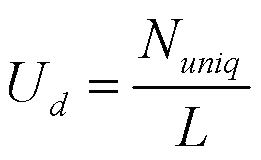 (1)
(1) 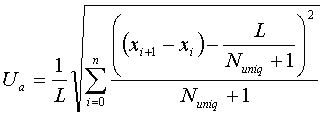 (2)
(2) 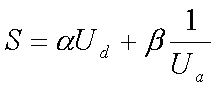 (3)
(3)