Install JDK8 and Eclipse (or any IDE you have been familiar with, say IntelliJ) in your computer (desktop/laptop). You don't need to send me email for this lab unless you cannot complete the installation.
Write a program for number-guessing game (you may refer to Guess the Number if you have never played this game). The program first generates a secret number ranging between 0 and 99, inclusive. Then the program asks the player to guess a number. If the input value is equal to the secret number, then the player wins. If not, then update the range depending on the input accordingly. (For example, assume that the secret number is 42. If the player types 50 for the first time, then the program shows (0, 49) on the screen.) When there is only one integer left, the player loses the game. Also, make sure that the player types a number in the feasible range; otherwise, ask the user to redo the input.
- Lab 1-1 (optional)
- Lab 1-2 (optional)
Modify the game loop which allows the player to guess at most 7 times. (Why 7 times?)
Add some strategies (AI?) to play this game and calculate each winning rate by using these strategies for 1e5 times. For example, the naive strategy is to guess a number in random, and its result is around 66%. Surprisingly, the winning rate for binary search is about 63%, not as expected to beat the naive one. Why?
Let N be the number of students, denoted by 0, 1, 2, ..., N − 1. First, implement an algorithm to generate a sequence of 0, 1, 2, ..., N − 1 in random order. Note that all elements in sequence are distinct. Second, write an algorithm to determine the number of groups among students and also report the members of each group. You may refer to the original problem statement in p. 7 of the slides. For example, consider N = 16 and the outputs are shown as follows.
Keyword: permutation index, cycle detection.
- Lab 2-1 (optional)
Replace the native array by ArrayList
First, implement three sorting algorithms (bubble sort, selection sort, and insertion sort) mentioned in class. Then compare the running time of these sorting algorithms together with Arrays.sort (check its API here). Since the performance of these comparison-based sorting algorithms is sensitive to the order of data sequence, I suggest that you could calculate the average running time for various sizes and make a benchmark for these four algorithms (using the doubling hypothesis), shown as below.
You may use System.currentTimeMillis() or System.nanoTime() to make timestamps (remember to use long variables). Note that the actual numbers in the table may differ from mine due to variety of runtime environments. If you are interested, you may watch this video for 15 sorting algorithms.
- Lab 3-1
- Lab 3-2 (optional)
- Lab 3-3 (optional)
- Lab 3-4 (optional)
- Lab 3-5 (optional)
Compare the growth rate of running time for each sorting algorithm to the theoretical prediction by big-O. Recall that the first three sorting algorithms runs in O(n ^ 2) time while Arrays.sort() runs in O(n log n) time.
Implement the algorithm of cocktail sort which runs in O(n ^ 2) time. You may refer to cocktail sort in Wikipedia.
Implement Shell's sorting algorithm which runs in O(n (log n) ^ 2) time. You may refer to shell sort in Wikipedia, or this article.
Implement the merge sort algorithm which runs in O(n log n) time. You may refer to merge sort in Wikipedia.
Implement the quick sort algorithm which runs in Θ(n log n) time. You may refer to quick sort in Wikipedia.
Let x be any real number and n be any nonnegative integer. Write a program which calculates x ^ n by recursion. For example, 2 ^ 10 = 1024. Try to make your program run in O(log n) time. Note that you are not allowed to use Math.pow() and any loop in your solution.
Keyword: exponentiation by squaring.
- Lab 4-1 (optional)
- Lab 4-2 (optional)
- Lab 4-3 (optional)
- Lab 4-4 (optional)
- Lab 4-5 (optional)
- Lab 4-6 (optional)
Compare your solution to the naive method (running in O(n) time). Report the speedup.
As you can see, the double overflow occurs when the exp exceeds 1000. To calculate the correct numbers, you may use the class BigDecimal for arbitrary digits.
Modify your solution for negative n.
Convert the recursion version into the loop version.
Introduce bitwise operators (&) and shift operators (>>) to your solution.
Let M be any positive int value. Write a function to calculate x ^ n mod M for n = 10000000. You may use the polynomial remainder theorem (see here).
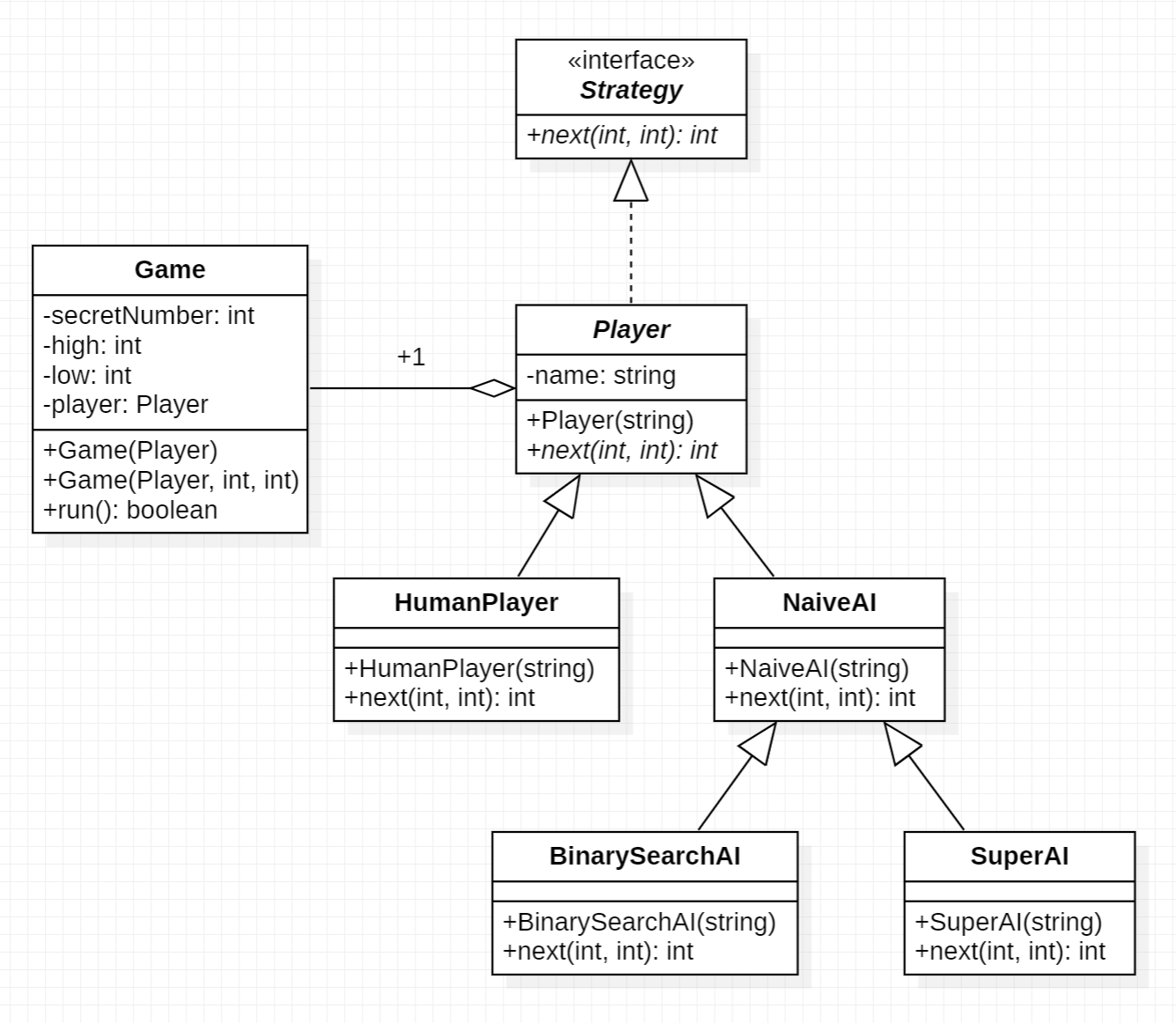
Rewrite your program of Lab 1 in OOP style. First analyze the functionalities in Lab 1 and then define any number of classes if necessary. For example, you could create two objects: one object is for the game procedure, the other object for the player. In this way, you should define a protocol so that the game has minimal dependency on the player. The resulting UML is shown below.
Keyword: OOP, class/interface inheritance, method overriding, subtype polymorphism, dependency injection, strategy pattern, observer pattern.
- Lab 5-1 (optional)
Try various strategies for this game. For example, the naive strategy is to guess a number in random, and the binary-search strategy is to return the number in the middle of the feasible range. Then compare the winning rates by simulating these strategies for 1e5 times.
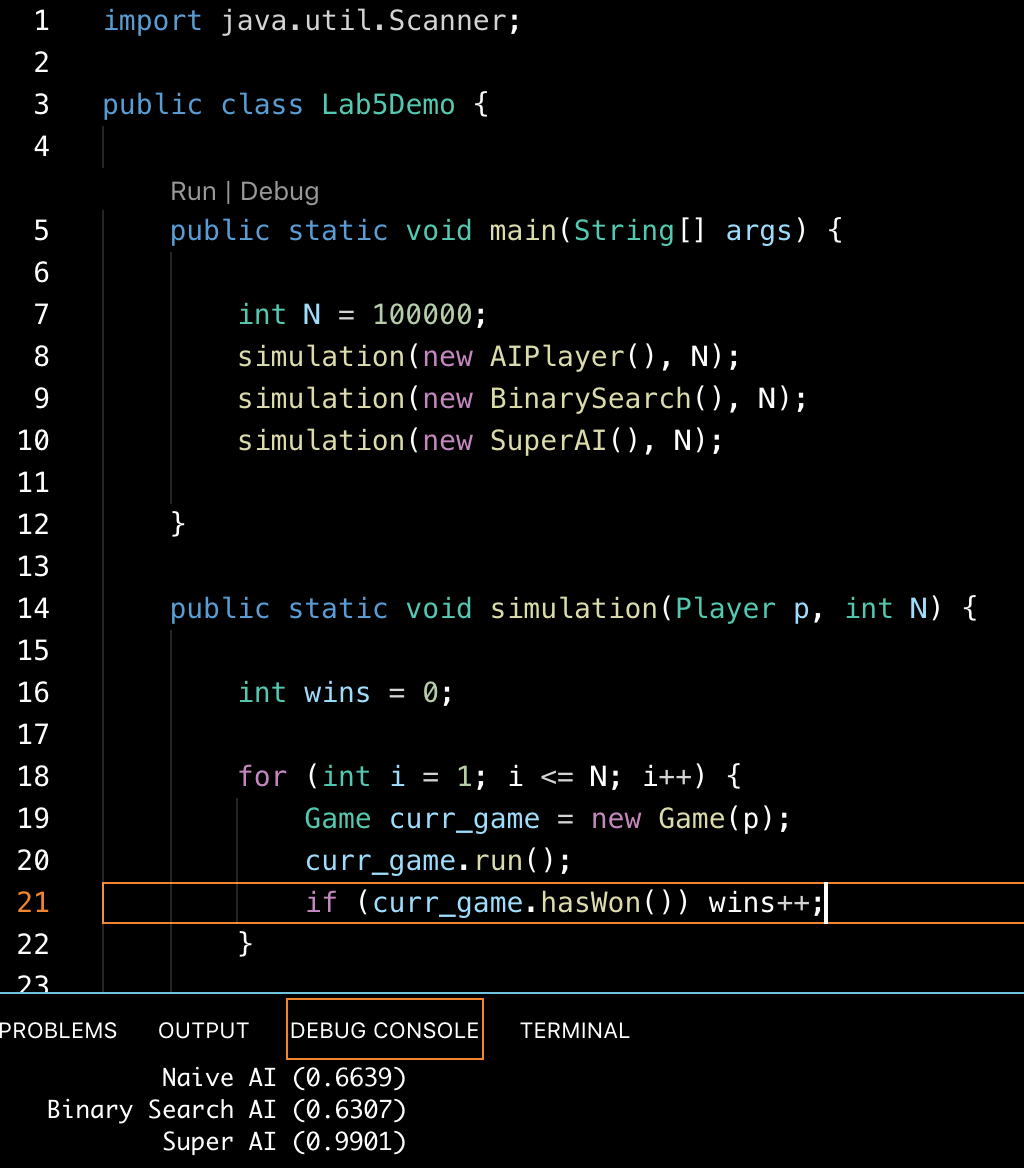
This snap shot is captured on Visual Studio Code.
The following problems interest me.
- Lab 6-1 (optional)
- Lab 6-2 (optional)
- Lab 6-3 (optional)
- Lab 6-4 (optional)
Write a program which estimates the Euler constant e ~ 2.7183 by Monte Carlo simulation. The procedure is as follows: (1) Set N = 1e5 and M = 0; (2) for each iteration, find the minimal number k of random numbers which follows a standard uniform distribution (simply use Math.random() in this case) so that the sum of these random numbers is greater than 1; (3) do M += k; (4) then the estimator of e can be done by M / N.
Keyword: Monte Carlo, Euler constant.
Write a program which simulates the price movement of one stock by Monte Carlo simulation. The input is as follows: (1) S (spot price), (2) r (annual interest rate), (4) v (annual volatility), (5) T (time to maturity, year), (6) m (periods within T), (7) N (number of replicates). Now define dt = T/ m. For each time 0 < i <= m, calculate the future price S(i) by S(i) = S(i - 1) * exp((r − 0.5 * v ^ 2) * dt + v * sqrt(dt) * RANDN), where RANDN is a random variable following a standard normal distribution (use the method nextGaussian() of Random objects; see Random from Oracle). Repeat the procedure above for N times. Then draw all price paths on the canvas. You may refer to my solution: GBM.zip.
Keyword: Monte Carlo, geometric Brownian motion.
Write a program which calculates the price of European call options. The input is as follows: (1) S (spot price), (2) X (strike price), (3) T (time to maturity, year), (4) v (annual volatility), (5) r (annual interest rate), (6) N (sample size). The price of European call options can be done as follows: (1) Set N = 1e5 and the call price c = 0; (2) for each iteration, calculate the future price S' by S' = S * exp((r − 0.5 * v ^ 2) * T + v * sqrt(T) * RANDN), where RANDN is a random variable following a standard normal distribution (use the method nextGaussian() of Random objects; see Random from Oracle); (3) if S' − X > 0, do c += S' − X; (4) after N iterations, do c /= N. Finally, output the option price c. For example, the European call price is 14.2xxx for the case of S = 100, X = 100, T = 1, v = 0.3, r = 0.05.
Keyword: Monte Carlo, geometric Brownian motion, option price, Black-Scholes model.
Write a program to display all permutation of N distinct items.
Keyword: permutation, Heap's algorithm.