第十四章
例外處理
14.1 丟出例外
錯誤碼
例外
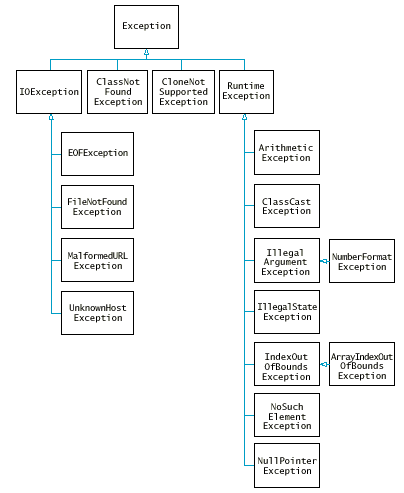
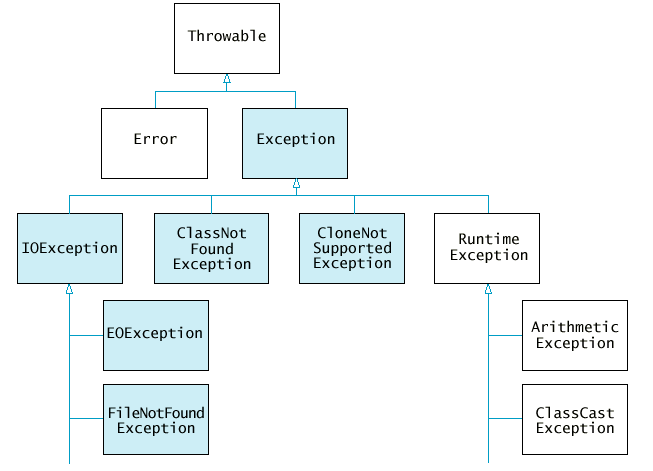
例外類別階層
Syntax 14.1: Throwing an Exception
Example:
| |
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
|
Purpose:
To throw an exception and transfer control to a handler for this exception
type |
14.2 受檢查的例外情形
- Compiler 檢查是否注意到例外情形
- 通常用於甚至在正確的程式中也會發生的錯誤
- IOException 及其子類別都是受檢查的例外
- NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
, . . . 都是未受檢查的例外--這些都是 你的過錯 :-)
- 虛擬機器的錯誤 (例如 OutOfMemoryError) 也是未受檢查的
- 這種區分並不完美. 例如, Integer.parseInt
丟出未受檢查的 NumberFormatException
- 不屬於 RuntimeException 的 Exception 所有子類別都是受檢查的例外
受檢查及未受檢查的例外
註明例外
Syntax 14.2: Exception Specification
| |
accessSpecifier returnType methodName(parameterType
parameterName, . . .)
throws ExceptionClass, ExceptionClass . . . |
Example:
| |
public void read(BufferedReader in) throws IOException |
Purpose:
To indicate the checked exceptions that a method can throw |
14.3 設計自己的例外型式
14.4 接住例外
每一例外都必須處理。 另一種例外處理方式是使用 try/catch 敘述。 把需要例外處理的程式碼放在 try 方塊內,
而把處理例外的程式碼放在 catch 方塊中。
try
{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("How old are you?");
String inputLine = in.readLine();
int age = Integer.parseInt(inputLine);
age++;
System.out.println("Next year,you'll be " + age);
}
catch (IOException exception)
{
System.out.println("Input/output error " +exception);
}
catch (NumberFormatException exception)
{
System.out.println("Input was not a number");
}
- 執行 try 方塊內的敘述
- 假如沒有例外發生, 跳過 catch 子句, 不執行
- 假如有例外發生, 跳到相對的 catch 子句執行
- 假如沒有相對的 catch 子句, 則丟給上一層的程式( calling 程式)
- 假如 main 未接住例外, 中止程式的執行
Syntax 14.3: General Try Block
| |
try
{
statement
statement
...
}
catch (ExceptionClass exceptionObject)
{
statement
statement
...
}
catch (ExceptionClass exceptionObject)
{
statement
statement
...
}
...
|
Example:
| |
try
{
System.out.println("What is your name?");
String name = console.readLine();
System.out.println("Hello,"+name +"!");
}
catch (IOException exception)
{
exception.printStackTrace();
System.exit(1);
}
|
Purpose:
To execute one or more statements that may generate exceptions. If
an exception of a particular type occurs, then stop executing those statements
and instead go to the matching catch clause. If no exception occurs, then
skip the catch clauses.
|
14.5 finally 子句
- 例外中止正在執行中的方法
- 危險: 有可能略過重要的程式碼
- 例如:
BufferedReader in;
in = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader(filename));
purse.read(in);
in.close();
即使例外發生, 也必須執行 in.close()
- 這種「無論如何」都必須執行的情形, 就要使用 finally 子句,
BufferedReader in = null;
try
{
in = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader(filename));
purse.read(in);
}
finally
{
if (in !=null) in.close();
}
- 當 try 方塊正常結束時執行。
- 假如 try 方塊內的敘述丟出例外, 在例外丟出 try 方塊之前執行。
- 也可以和 catch 子句一起使用
Syntax 14.4: finally 子句
| |
try
{
statement
statement
...
}
finally
{
statement
statement
...
}
|
Example:
| |
BufferedReader in = null;
try
{
in = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader(filename));
purse.read(in);
}
finally
{
if (in !=null) in.close();
}
|
Purpose:
To execute one or more statements that may generate exceptions, and
to execute the statements in the finally clause whether or not an
exception occured. |
14.6 完整的例題
- Program
- reads coin descriptions from file
- adds coins to purse
- prints total
- What can go wrong?
- File might not exist
- File might have data in wrong format
- Who can detect the faults?
- main method of PurseTest interacts with user
- main method can report errors
- Other methods pass exceptions to caller
The read method of the Coin class
- Distinguishes between expected and unexpected end of
file
public boolean read(BufferedReader in) throws IOException
{
String input =in.readLine();
if (input == null) // normal end of file
return false;
value = Double.parseDouble(input);
// may throw unchecked NumberFormatException
name = in.readLine();
if (name == null) // unexpected end of file
throw new EOFException("Coin name expected");
return true;
}
The read method of the Purse class
- Unconcerned with exceptions
- Just passes them to caller
public void read(BufferedReader in)
throws IOException
{
boolean done = false;
while (!done)
{
Coin c = new Coin();
if (c.read(in)) add(c);
else done =true;
}
}
The readFile method of the Purse class
- finally clause closes files if exception happens
public void readFile(String filename)
throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = null;
try
{
in = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader(filename));
read(in);
}
finally
{
if (in != null)
in.close();
}
}
User interaction in main
- If an exception occurs, user can specify another file name
boolean done = false;
String filename = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter file name");
while (!done)
{
try
{
Purse myPurse = new Purse();
myPurse.readFile(filename);
System.out.println("total=" + myPurse.getTotal());
done =true;
}
catch (IOException exception)
{
System.out.println("Input/output error " + exception);
}
catch (NumberFormatException exception)
{
exception.printStackTrace(); // error in file format
}
if (!done)
{
filename = JOptionPane.showInputDialog( "Try another file:");
if (filename == null)
done =true;
}
}
Scenario
- PurseTest.main calls Purse.readFile
- Purse.readFile calls Purse.read
- Purse.read calls Coin.read
- Coin.read throws an EOFException
- Coin.read has no handler for the exception and terminates
immediately.
- Purse.read has no handler for the exception and terminates
immediately
- Purse.readFile has no handler for the exception and terminates
immediately after executing the finally clause and closing the file.
- PurseTest.main has a handler for an IOException ,
a superclass of EOFException. That handler prints a message to the
user. Afterwards, the user is given another chance to enter a file name.
Note that the statement printing the purse total has been skipped.
File PurseTest.java
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
This program prompts the user to enter a file name
with coin values. A purse object is filled with
the coins specified in the file. In case of an exception,
the user can choose another file.
*/
public class PurseTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
boolean done = false;
String filename
= JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Enter file name");
while (!done)
{
try
{
Purse myPurse = new Purse();
myPurse.readFile(filename);
System.out.println("total=" + myPurse.getTotal());
done = true;
}
catch (IOException exception)
{
System.out.println("Input/output error " + exception);
}
catch (NumberFormatException exception)
{
exception.printStackTrace();
}
if (!done)
{
filename = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(
"Try another file:");
if (filename == null) done = true;
}
}
System.exit(0);
}
}
File Purse.java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
A purse computes the total of a collection of coins.
*/
public class Purse
{
/**
Constructs an empty purse.
*/
public Purse()
{
total = 0;
}
/**
Read a file with coin descriptions and adds the coins
to the purse.
@param filename the name of the file
*/
public void readFile(String filename)
throws IOException
{
BufferedReader in = null;
try
{
in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filename));
read(in);
}
finally
{
if (in != null) in.close();
}
}
/**
Read a file with coin descriptions and adds the coins
to the purse.
@param in the buffered reader for reading the input
*/
public void read(BufferedReader in)
throws IOException
{
boolean done = false;
while (!done)
{
Coin c = new Coin();
if (c.read(in))
add(c);
else
done = true;
}
}
/**
Add a coin to the purse.
@param aCoin the coin to add
*/
public void add(Coin aCoin)
{
total = total + aCoin.getValue();
}
/**
Get the total value of the coins in the purse.
@return the sum of all coin values
*/
public double getTotal()
{
return total;
}
private double total;
}
File Coin.java
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.EOFException;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
A coin with a monetary value.
*/
public class Coin
{
/**
Constructs a default coin.
Use the read method to fill in the value and name.
*/
public Coin()
{
value = 0;
name = "";
}
/**
Constructs a coin.
@param aValue the monetary value of the coin.
@param aName the name of the coin
*/
public Coin(double aValue, String aName)
{
value = aValue;
name = aName;
}
/**
Reads a coin value and name.
@param in the reader
@return true if the data was read,
false if the end of the stream was reached
*/
public boolean read(BufferedReader in)
throws IOException
{
String input = in.readLine();
if (input == null) return false;
value = Double.parseDouble(input);
name = in.readLine();
if (name == null)
throw new EOFException("Coin name expected");
return true;
}
/**
Gets the coin value.
@return the value
*/
public double getValue()
{
return value;
}
/**
Gets the coin name.
@return the name
*/
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
private double value;
private String name;
}

