第十三章
陣列串列和陣列
13,1 陣列串列(Array List)
取得陣列串列的元件
逐步取得所有的元件
for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); i++)
{
Coin c = (Coin)coins.get(i);
do something with c
}
添加和移除元件
- set 覆寫己有的值,
coins.set(4, aNickel);
- add 在指標之前添加新值,
coins.add(i, c)
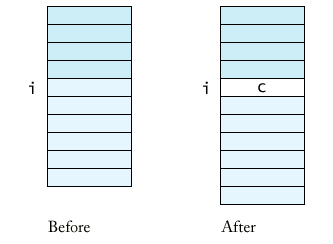
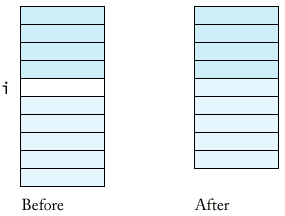
- remove 在指標處移除一元件
coins.remove(i)
File Purse.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
A purse holds a collection of coins.
*/
public class Purse
{
/**
Constructs an empty purse.
*/
public Purse()
{
coins = new ArrayList();
}
/**
Add a coin to the purse.
@param aCoin the coin to add
*/
public void add(Coin aCoin)
{
coins.add(aCoin);
}
/**
Get the total value of the coins in the purse.
@return the sum of all coin values
*/
public double getTotal()
{
double total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); i++)
{
Coin aCoin = (Coin)coins.get(i);
total = total + aCoin.getValue();
}
return total;
}
private ArrayList coins;
}
13.2 簡單的陣列串列演算法
Linear Search Algorithm
public class Purse
{
public boolean find(Coin aCoin)
{
for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); i++)
{
Coin c =(Coin)coins.get(i);
if (c.equals(aCoin)) return true; //found a match
}
return false; //no match in the entire array list
}
...
}
Counting
public class Purse
{
public int count(Coin aCoin)
{
int matches = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); i++)
{
Coin c =(Coin)coins.get(i);
if (c.equals(aCoin)) matches++; //found a match
}
return matches;
}
...
}
Finding Maximum
public class Purse
{
public Coin getMaximum()
{
Coin max =(Coin)coins.get(0);
for (int i = 1; i <coins.size(); i++) // loop starts at 1
{
Coin c =(Coin)coins.get(i);
if (c.getValue()>max.getValue()) max =c;
}
return max;
}
...
}
File Purse.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
A purse holds a collection of coins.
*/
public class Purse
{
/**
Constructs an empty purse.
*/
public Purse()
{
coins = new ArrayList();
}
/**
Add a coin to the purse.
@param aCoin the coin to add
*/
public void add(Coin aCoin)
{
coins.add(aCoin);
}
/**
Get the total value of the coins in the purse.
@return the sum of all coin values
*/
public double getTotal()
{
double total = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); i++)
{
Coin aCoin = (Coin)coins.get(i);
total = total + aCoin.getValue();
}
return total;
}
/**
Counts the number of coins in the purse
@return the number of coins
*/
public int count()
{
return coins.size();
}
/**
Tests if the purse has a coin that matches
a given coin.
@param aCoin the coin to match
@return true if there is a coin equal to aCoin
*/
public boolean find(Coin aCoin)
{
for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); i++)
{
Coin c = (Coin)coins.get(i);
if (c.equals(aCoin)) return true; // found a match
}
return false; // no match in the entire array list
}
/**
Counts the number of coins in the purse that match
a given coin.
@param aCoin the coin to match
@return the number of coins equal to aCoin
*/
public int count(Coin aCoin)
{
int matches = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < coins.size(); i++)
{
Coin c = (Coin)coins.get(i);
if (c.equals(aCoin)) matches++; // found a match
}
return matches;
}
/**
Finds the coin with the largest value.
(Precondition: The purse is not empty)
@return a coin with maximum value in this purse
*/
Coin getMaximum()
{
Coin max = (Coin)coins.get(0);
for (int i = 1; i < coins.size(); i++)
{
Coin c = (Coin)coins.get(i);
if (c.getValue() > max.getValue())
max = c;
}
return max;
}
private ArrayList coins;
}
13.3 儲存數字於陣列串列
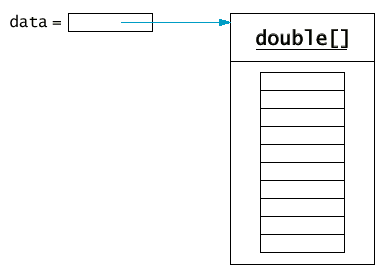
13.4 陣列
Syntax 13.1: Array Construction
Example:
Purpose:To construct an array with a given number of elements.
|
Syntax 13.2: Array Element Access
Example:
| |
a[4] = 29.95;
double x = a[4]; |
Purpose:To access an element in an array |
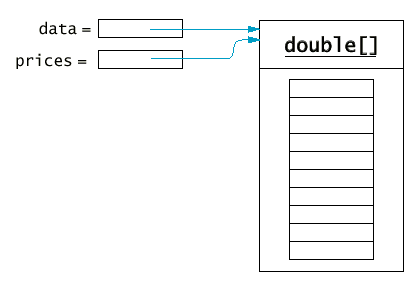
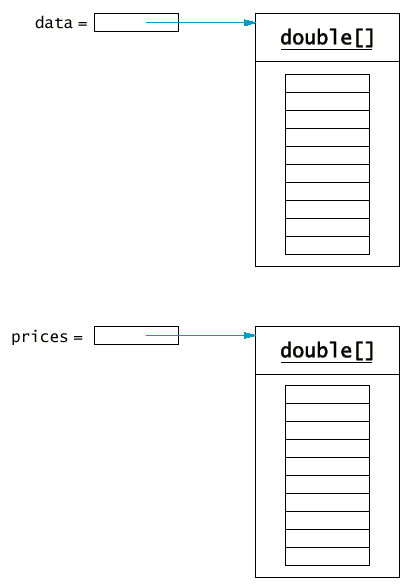
13.5 複製陣列
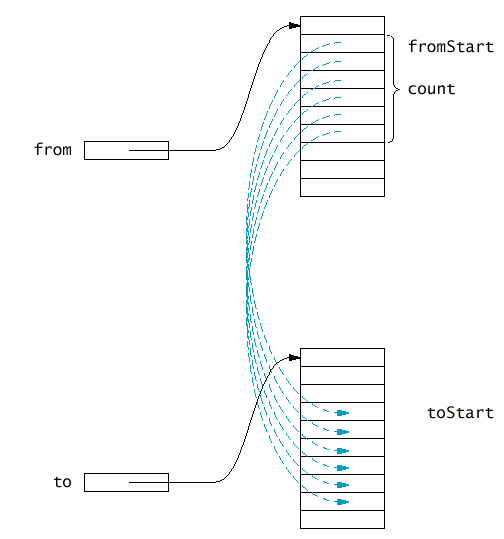
複製陣列的元件
System.arraycopy(from, fromStart, to, toStart, count);
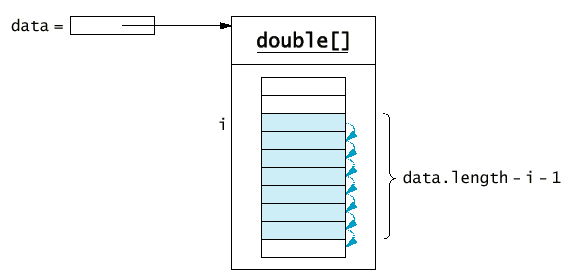
添加和移除陣列元件
- 添加元件:
System.arraycopy(data, i, data, i + 1, data.length - i - 1);
data[i] = x;
- 移除元件:
System.arraycopy(data, i + 1, data, i, data.length - i - 1);
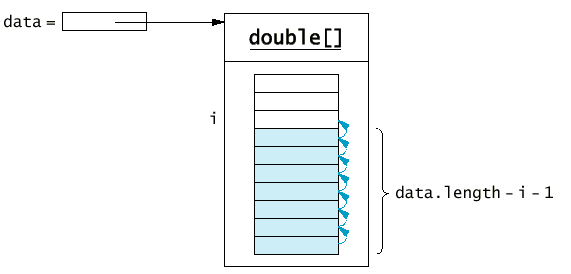
13.6 部分有值的陣列
- 陣列長度 = 陣列能容納的最多元件數
- 通常陣列只有部分有值
- 需要變數記錄目前大小
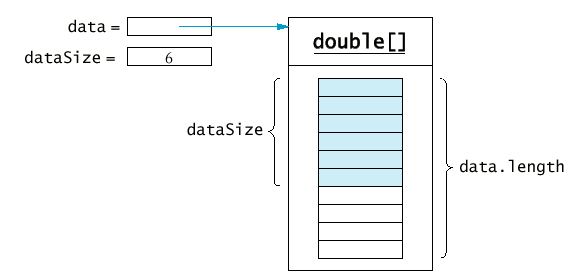
- 一致的命名慣例:
final int DATA_LENGTH = 100;
double[] data = new double[DATA_LENGTH];
int dataSize = 0;
- 當陣列有元件設值, 要更新 dataSize:
data[dataSize] = x;
dataSize++;
- 存取陣列元件時, 記得要停在 dataSize:
for (int i = 0; i < dataSize; i++)
sum = sum + data[i];
- 小心不要超出陣列的指標範圍,
if (dataSize >= data.length)
System.out.println("Sorry--array full");
- 或用增長陣列來解決:
double newData = new double[2 * data.length];
System.arraycopy(data, 0, newData, 0, data.length);
data = newData;
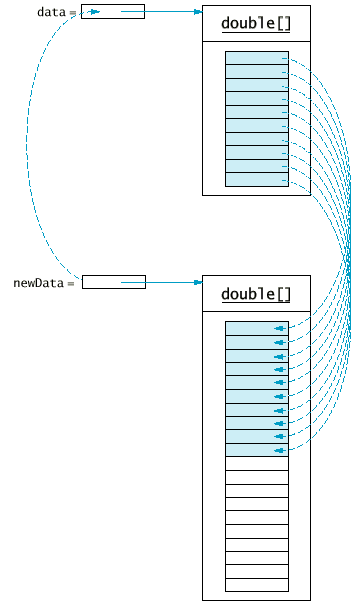
File DataSet.java
/**
This class computes the average of a set of data values.
*/
public class DataSet
{
/**
Constructs an empty data set.
*/
public DataSet()
{
final int DATA_LENGTH = 100;
data = new double[DATA_LENGTH];
dataSize = 0;
}
/**
Adds a data value to the data set
@param x a data value
*/
public void add(double x)
{
if (dataSize >= data.length)
{
// make a new array of twice the size
double[] newData = new double[2 * data.length];
// copy over all elements from data to newData
System.arraycopy(data, 0, newData, 0, data.length);
// abandon the old array and store in data
// a reference to the new array
data = newData;
}
data[dataSize] = x;
dataSize++;
}
/**
Gets the average of the added data.
@return the average or 0 if no data has been added
*/
public double getAverage()
{
if (dataSize == 0) return 0;
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dataSize; i++)
sum = sum + data[i];
return sum / dataSize;
}
private double[] data;
private int dataSize;
}
File DataSetTest.java
import java.util.Random;
/**
This program tests the DataSet class by adding 10,000 numbers
to the data set and computing the average.
*/
public class DataSetTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Random generator = new Random();
DataSet data = new DataSet();
final int COUNT = 10000;
System.out.println("Adding " + COUNT + " random numbers.");
for (int i = 0; i < COUNT; i++)
{
double x = generator.nextDouble();
data.add(x);
}
double average = data.getAverage();
System.out.println("average=" + average);
}
}
13.7 二維陣列
File TicTacToe.java
/**
A 3 x 3 Tic-Tac-Toe board.
*/
public class TicTacToe
{
/**
Constructs an empty board.
*/
public TicTacToe()
{
board = new char[ROWS][COLUMNS];
// fill with spaces
for (int i = 0; i < ROWS; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < COLUMNS; j++)
board[i][j] = ' ';
}
/**
Sets a field in the board. The field must be unoccupied.
@param i the row index
@param j the column index
@param player the player ('x' or 'o')
*/
public void set(int i, int j, char player)
{
if (board[i][j] != ' ')
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Position occupied");
board[i][j] = player;
}
/**
Creates a string representation of the board such as
|x o|
| x |
| o|
@return the string representation
*/
public String toString()
{
String r = "";
for (int i = 0; i < ROWS; i++)
{
r = r + "|";
for (int j = 0; j < COLUMNS; j++)
r = r + board[i][j];
r = r + "|\n";
}
return r;
}
private char[][] board;
private static final int ROWS = 3;
private static final int COLUMNS = 3;
}
File TicTacToeTest.java
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
/**
This program tests the TicTacToe class by prompting the
user to set positions on the board and printing out the
result.
*/
public class TicTacToeTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char player = 'x';
TicTacToe game = new TicTacToe();
while (true)
{
System.out.println(game); // calls game.toString()
String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(
"Row for " + player + " (Cancel to exit)");
if (input == null) System.exit(0);
int row = Integer.parseInt(input);
input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog(
"Column for " + player);
int column = Integer.parseInt(input);
game.set(row, column, player);
if (player == 'x') player = 'o'; else player = 'x';
}
}
}