第二章
物件和類別簡介
2.1 物件和類別
- 物件(object): entity that you can manipulate in your programs (by invoking
methods)
- 每一物件都屬於某一類別(class)
- 類別: 一組具有相同行為的物件集合
- 類別決定有那些方法可以使用, 如
"Hello".println() // Error
"Hello".length() // OK
Rectangle Class
- Construct a rectangle:
new Rectangle(5, 10, 20, 30)
new Rectangle()
- Use the constructed object
System.out.println(new Rectangle(5, 10, 20, 30));
prints
java.awt.Rectangle[x=5,y=10,width=20,height=30]
Rectangle Shapes
A Rectangle Object
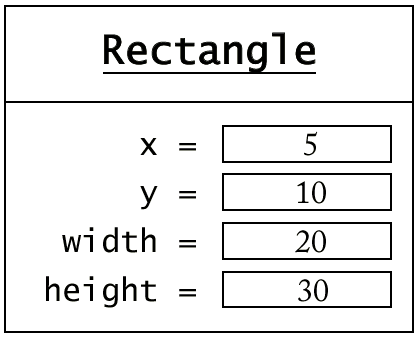
Syntax 2.1: Object Construction
| |
new ClassName(parameters)
|
Example:
| |
new Rectangle(5, 10, 20, 30)
new Car("BMW 540ti", 2004)
|
Purpose:
To construct a new object, initialize it with the construction parameters,
and return a reference to the constructed object. |
2.2 Object Variables
- Declare and optionally initialize:
Rectangle cerealBox = new Rectangle(5, 10, 20, 30);
Rectangle crispyCrunchy;
- Apply methods:
cerealBox.translate(15, 25);
- Share objects:
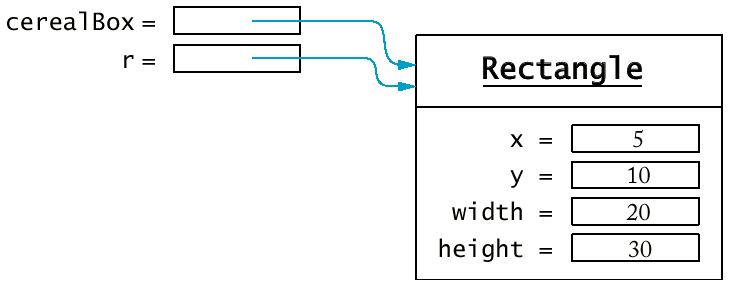
r = cerealBox;
Uninitialized and Initialized Variables
Uninitialized:
Initialized:
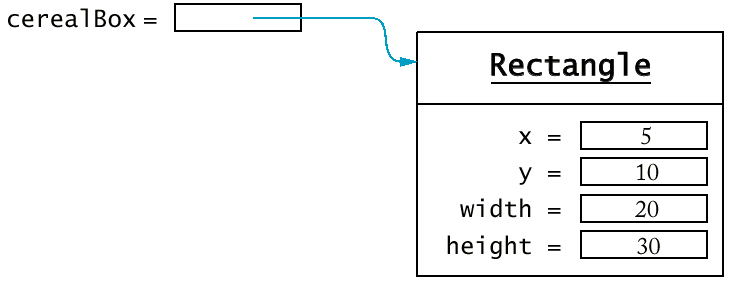
兩個物件變數指到同一物件
Syntax 2.2: Variable Definition
| |
TypeName variableName;
TypeName variableName = expression;
|
Example:
| |
Rectangle cerealBox;
String name ="Dave"; |
Purpose:
To define a new variable of a particular type and optionally supply an initial
value |
寫一測試程式
Java 應用程式(Application)
由一組類別(class)構成, 其中有一主類別。執行程式指執行在 main 類別中的方法(或稱函式) main。
- 界定一主類別, 例如 MoveTest
- 提供一 main 方法
- 在 main 方法內, 寫碼實現所要做的工作
- 引入(import) Java 的庫存類別, 如:
import java.awt.Rectangle;
java.awt 是package, 而 Rectangle是其中的一個類別
- java.lang 中的 package, 如
String 和 System, 不需引入
Syntax 2.3 : Importing a Class from a Package
| |
import packageName.ClassName
;
|
Example:
| |
import java.awt.Rectangle; |
Purpose:
To import a class from a package for use in a program.
|
File MoveTest.java
import java.awt.Rectangle;
public class MoveTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Rectangle cerealBox = new Rectangle(5, 10, 20, 30);
// move the rectangle
cerealBox.translate(15, 25);
// print the moved rectangle
System.out.println(cerealBox);
}
}
界定類別
一個簡單類別
public class Greeter
{
public String sayHello()
{
String message ="Hello,World!";
return message;
}
}
方法的界定
- access specifier (such as public)
- return type (such as String or void)
- method name (such as sayHello)
- list of parameters (empty for sayHello)
- method body in { }
方法參數
public class Rectangle
{
. . .
public void translate(int x, int y)
{
method body
}
. . .
}
Syntax 2.4: Method Implementation
public class ClassName
{
...
accessSpecifier returnType methodName(parameterType parameterName,...)
{
method body
}
...
}
|
|
Example:
| |
public class Greeter
{
public String sayHello()
{
String message ="Hello,World!";
return message;
}
}
|
Purpose:
To define the behavior of a method A method definition specifies the method
name, parameters, and the statements for carrying out the method's actions.
|
Syntax 2.5: The return Statement
| |
return expression;
or
return; |
Example:
Purpose:
To specify the value that a method returns, and exit the method immediately.
The return value becomes the value of the method call expression.
|
2.4 測試一類別
- 測試用的類別(Test class): 一類別,其中的 main 方法含有測試另一類別的敘述。
- 通常進行下列步驟:
- 建構一個或更多屬於要測試類別的物件。
- 引用(invoke)一個或更多方法。
- 列出一個或更多的結果。
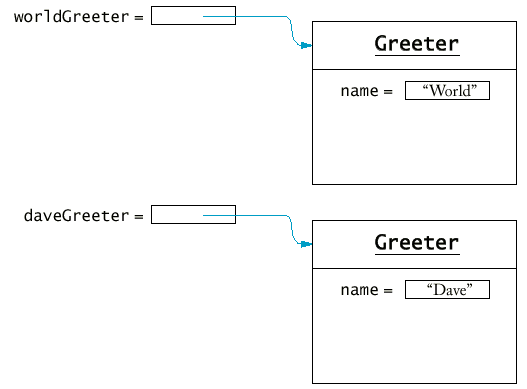
A Test Class for the Greeter Class
public class GreeterTest
{
public static void main(String [] args))
{
Greeter worldGreeter = new Greeter();
System.out.println(worldGreeter.sayHello());
}
}
說明:
- 字串類別用 String 。
- System.out 為類別 printStream 的個例(instance), println 為其方法。
建造測試用的程式
- 造一新目錄以便容納所寫的程式。
- 造二個檔案, 一個儲存要測試的類別程式碼(如 Greeter.java), 另一個儲存測試用的類別(如 GreeterTest.java)。
- 編譯這兩個程式檔。
- 執行測試用的程式。
使用爪哇系統設計工具(Java System Design Kit)測試
用法
- 編譯:
- javac Greeter.java
- javac GreeterTest.java
- 執行: java GreeterTest
注意:
- 編譯時檔名要有 extension, 執行時檔名不要有 extension (預設為 .class)。
- 編譯時, 檔名和類別名稱必須相同, 大小寫要一致。
mkdir greeter
cd greeter
edit Greeter.java
edit GreeterTest.java
javac Greeter.java
javac GreeterTest.java
java GreeterTest
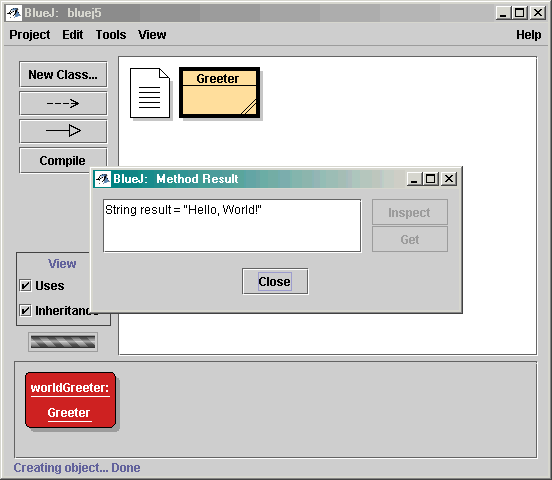
使用 BlueJ 測試
2.5 Instance Fields
public class Greeter
{
...
private String name;
}
- access specifier (such as private)
- type of variable (such as String)
- name of variable (such as name)
Instance Fields
Accessing Instance Fields
- The sayHello method of the Greeter class can access
the private instance field:
public String sayHello()
{
String message = "Hello, " + name + "!";
return message;
}
- Other methods cannot:
public class GreeterTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
. . .
System.out.println(daveGreeter.name); // ERROR
}
}
- Encapsulation = Hiding data and providing access through methods
Syntax 2.6 : Instance Field Declaration
| |
accessSpecifier class ClassName
{
...
accessSpecifier fieldType fieldName;
...
}
|
Example:
| |
public class Greeter
{
...
private String name;
...
}
|
Purpose:
To define a field that is present in every object of a class
|
2.6 Constructors
Syntax 2.7 : Constructor Implementation
| |
accessSpecifier class ClassName
{
...
accessSpecifier ClassName(parameterType
parameterName ...)
{
constructor implementation
}
...
}
|
Example:
| |
public class Greeter
{
...
public Greeter(String aName)
{
name = aName;
}
...
}
|
Purpose:
To define the behavior of a constructor, which is used to initialize the
instance fields of newly created objects
|
File Greeter.java
public class Greeter
{
public Greeter(String aName)
{
name = aName;
}
public String sayHello()
{
String message = "Hello, " + name + "!";
return message;
}
private String name;
}
2.7 設計公用界面
Behavior of bank account:
- 存款(deposit)
- 提款(withdraw)
- 查詢餘額(balance)
Methods of BankAccount class:
- deposit
- withdraw
- getBalance
BankAccount Public Interface
public BankAccount()
public BankAccount(double initialBalance)
public void deposit(double amount)
public void withdraw(double amount)
public double getBalance()
使用公用界面
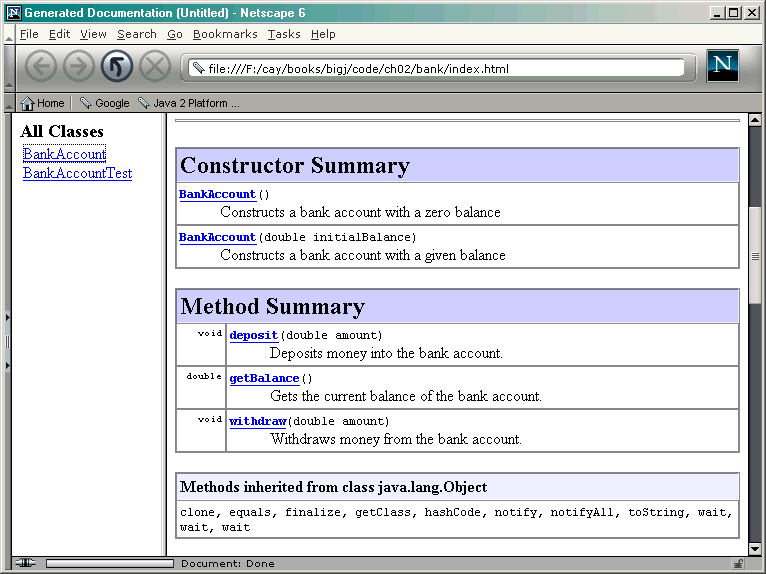
2.8 註解公用界面
/**
Withdraws money from the bank account.
@param the amount to withdraw
*/
public void withdraw(double amount)
{
implementation filled in later
}
/**
Gets the current balance of the bank account.
@return the current balance
*/
public double getBalance()
{
implementation filled in later
}
註解類別
/**
A bank account has a balance that can
be changed by deposits and withdrawals.
*/
public class BankAccount
{
...
}
Javadoc Method Summary
Javadoc Method Detail
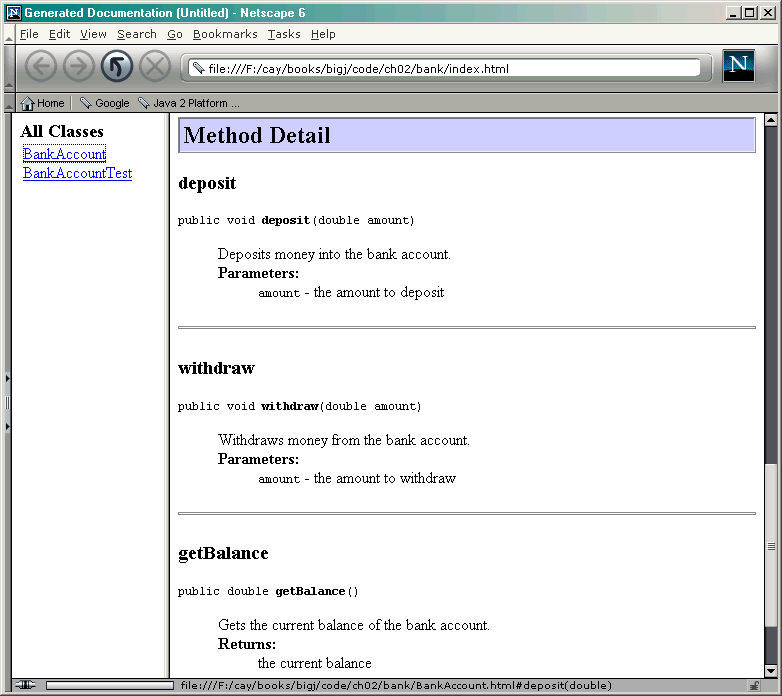
2.9 實現類別
實現 BankAccount 類別
- 界定用以保存物件狀態的個例變數(instance variable)
private double balance
- 實現方法和建構式(constructor)
File BankAccount.java
/**
A bank account has a balance that can be changed by
deposits and withdrawals.
*/
public class BankAccount
{
/**
Constructs a bank account with a zero balance
*/
public BankAccount()
{
balance = 0;
}
/**
Constructs a bank account with a given balance
@param initialBalance the initial balance
*/
public BankAccount(double initialBalance)
{
balance = initialBalance;
}
/**
Deposits money into the bank account.
@param amount the amount to deposit
*/
public void deposit(double amount)
{
double newBalance = balance + amount;
balance = newBalance;
}
/**
Withdraws money from the bank account.
@param amount the amount to withdraw
*/
public void withdraw(double amount)
{
double newBalance = balance - amount;
balance = newBalance;
}
/**
Gets the current balance of the bank account.
@return the current balance
*/
public double getBalance()
{
return balance;
}
private double balance;
}
File BankAccountTest.java
/**
A class to test the BankAccount class.
*/
public class BankAccountTest
{
/**
Tests the methods of the BankAccount class.
@param args not used
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
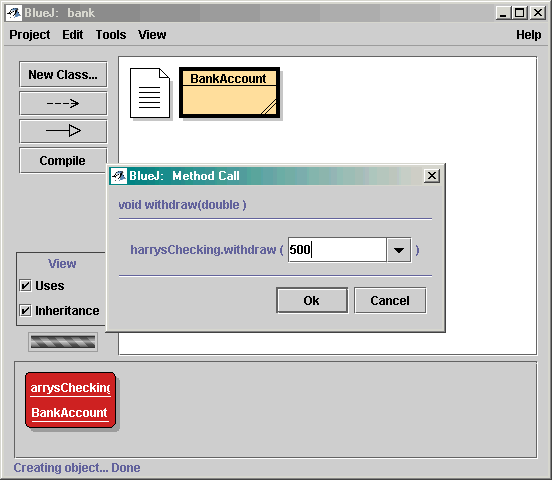
BankAccount harrysChecking = new BankAccount();
harrysChecking.deposit(2000);
harrysChecking.withdraw(500);
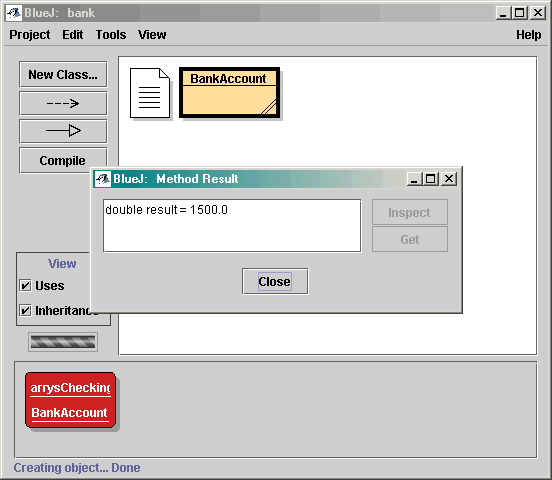
System.out.println(harrysChecking.getBalance());
}
}
在 BlueJ 引用方法
The Method Return Value in BlueJ
2.10 變數型式
- Instance fields (balance in BankAccount)
belong to an object
- Local variables (newBalance in deposit method)
belong to a method
must be initialized
- Parameter variables (amount in deposit method)
belong to a method
initialized in a method call
public class BankAccount
{
...
public void deposit(double amount) // parameter varialbe
{
double newBalance = balance + amount; // local varialbe
balance = newBalance;
}
public void withdraw(double amount) // ? varialbe
{
double newBalance = balance - amount; // ? varialbe
balance = newBalance;
}
public double getBalance()
{
return balance; // ? varialbe
}
private double balance; // instance varialbe
}
2.11 Explicit and Implicit Parameters
public void withdraw(double amount)
{
double newBalance = balance - amount;
balance = newBalance;
}
- explicit: amount
- implicit: the bank account object
balance is the balance of the object momsSavings:
momsSavings.withdraw(500)
means
double newBalance = momsSavings.balance - amount;
momsSavings.balance = newBalance;
implicit 參數可用this表明, 如
public void deposit(double amount)
{
double newBalance = this.balance + amount;
this.balance = newBalance;
}









